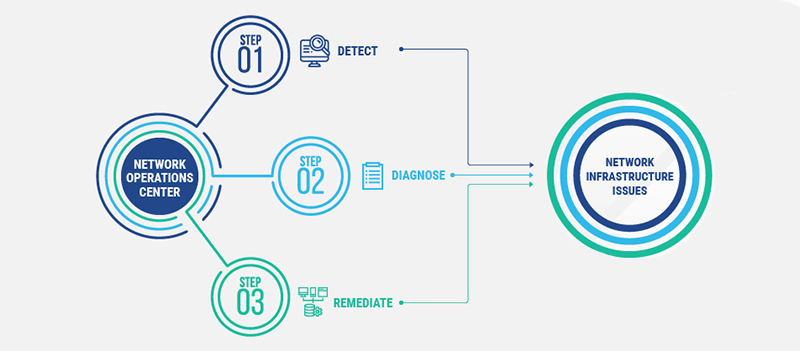
What is a Network Operations Center?
A network operations center (NOC) is a centralized location where 24/7 monitoring and management of events affecting technology services and infrastructure of an organization takes place. Therefore, NOC serves as the first line of defense against network disruptions and failures. Through the NOC, organizations gain full visibility into their network, so they can detect anomalies and either take steps to prevent problems or quickly resolve issues as they emerge. The NOC can be managed by the company, by a direct service provider or by an outsourced third party.
Why a NOC is needed?
[Resource: https://www.extnoc.com/network-operations-center]
Smaller organizations might not need a NOC, but larger companies and enterprises find it worthy to have a NOC to run the operations better. The following are a few purposes to have a NOC.
- Monitoring the network for detect problems, including those originating from outside sources
- Server, network and device management, including software installation, updates, troubleshooting devices
- Respond to incidents like power failures and communication line failures
- Backup and storage for disaster recovery purposes
- Patch management
- Managing firewalls, intrusion prevention system management and antivirus support for network devices
- Policy enforcement related to network management
What happens at NOC?
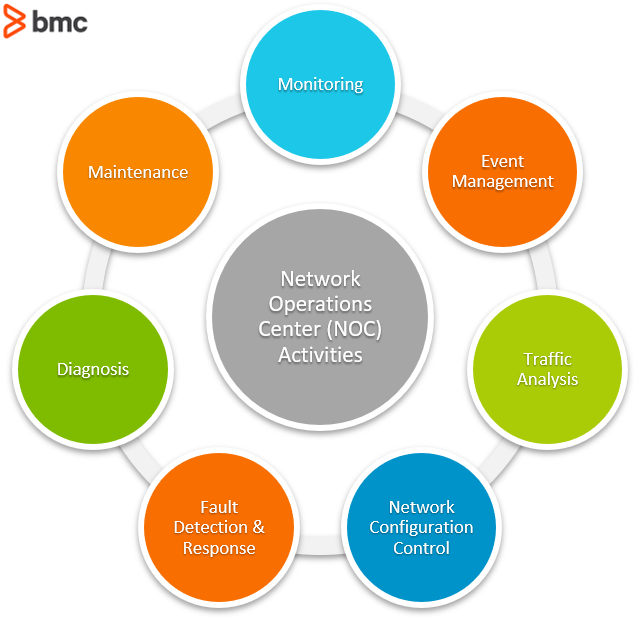
NOC basically supports live services, services about to be deployed and monitors networking equipment (eg. routers, switches, servers), power, transactions, traffic, user patterns etc. So monitoring and event management are the 2 main activities of a NOC.
Monitoring:
Mainly focuses on detecting conditions of potential significance in configuration items, tracking and recording the state of different networking components as well as providing that information to relevant parties of the organization.
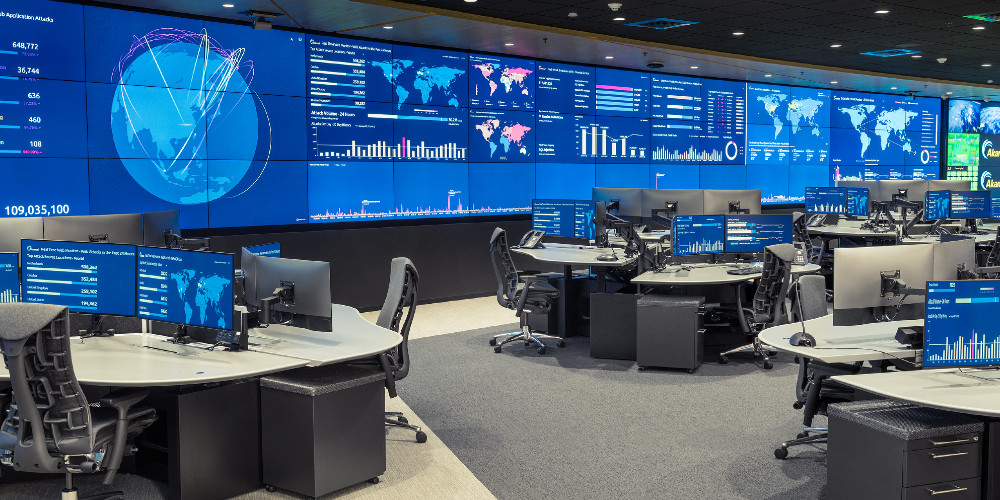
Large screens, monitors, consoles for sharing key indicators like traffic and node status and for viewing specific elements of networks are often seen at a NOC. More often the main screens show outputs from a centralized monitoring system that gathers, synthesizes, and correlates data from numerous sources related to networks of the organization. The operator monitors and smaller screens display event information like status, source, time.
Event management:
Analyzes those monitored changes of state which can be defined as an event, determine the significance of the changes to identify and initialize the correct response to the event is done in the event management process. Through this NOC helps to maintain optimal network performance and availability, as well as to ensure continuous uptime.
NOC has different collaboration tools, reporting tools, service management software (for logging and escalating significant events), software for remote access and troubleshooting, to improve the efficiency of the event management process.
Other than these main activities, NOC performs:
- Traffic analysis
- Network configuration control
- Fault detection
- Diagnosis and Maintenance
[Resource: https://www.bmc.com/blogs/noc-network-operations-center]
The NOC Team
The NOC team has technicians – NOC engineers, analysts, team leaders/supervisors and operators. NOC staff require specific skill sets in monitoring, maintaining and quickly resolving performance issues within the network. NOC technicians usually have significant work experience, specifically in network monitoring and tools. The scope of a NOC engineer’s job can be altered depending on the service provider’s service offerings and infrastructure layout of the organization.
Following are some skills needed for a NOC engineer
- Knowledge of service architecture, design, resource configuration
- Expertise in monitoring tools, IT Service Management tools, backup and data recovery tools
- Knowledge of network and device troubleshooting
- Knowledge of incident models, diagnostic tools, methods
- Analytical and communication skills
NOC Best practices
With the complexities involved with today’s networks and services, network operations staff face many challenges at a NOC. Since NOC plays an important role to keep networks and services attached to it up and running 24/7 it is always better to follow best practices to avoid troubles and difficulties. Here are some good practices to keep in mind when implementing a NOC.
Select proper NOC design and network management architecture
When it comes to setting up a NOC, it is important to consider both people and the environment. Spacious design to allow airflow, comfort and easy mobility will provide a better working environment for the NOC team. Redundancy for power and connectivity to ensure unhindered 24/7 operations as well as scalability to support future growth needs for people or equipment are also needed to be considered. There are different network management architectures like centralized, distributed or hierarchical. The best suitable architecture can be chosen based on the organization’s requirements as well as resources.
Recognizing and prioritizing incidents based on business requirements, organizational policies and operational impact
It is always important to consider the organizational policies as well as business and operational impact for any incident identified. High priority is needed for incidents with more critical impacts and proper methodology needs to be followed to evaluate the impacts.
Documenting all actions following standard company policies and procedures
Following standard protocols and procedures will minimize the difficulty in sharing information with other parties and understanding the documents.
This was a simple overview of what a network operations centre is and what happens there in a NOC. So it is clear that a NOC plays a significant role in organizations to keep operations running smoothly or minimize business and other impacts in case of any incidents that affect the organization’s networks.